You might wonder, how do electric bikes work? Electric bikes use a motor and battery to help you ride farther and faster with less effort. When you pedal an electric bike, the motor gives you extra power, making hills and long trips much easier. Many riders switch to e-bikes because they want a fun, easy, and eco-friendly way to travel.
In 2022, nearly 47 million e-bikes were sold worldwide, showing just how popular they have become. People choose electric bikes for smooth commutes, carrying groceries, and enjoying outdoor rides without feeling tired. With so many options, you can find an electric bike that fits your needs and lifestyle. E-bikes keep growing in popularity as technology improves and more people look for better ways to get around.
-
Electric bikes use a motor and battery to give you extra power, making pedaling easier and rides longer.
-
Main parts like the motor, battery, sensors, and controller work together to provide smooth and safe assistance.
-
Pedal assist helps you ride with less effort by adding power when you pedal, while throttle mode lets you ride without pedaling but uses more battery.
-
Choosing the right support level and maintaining your e-bike properly can improve battery life and riding experience.
-
Always wear a helmet, follow local laws, and check your bike before riding to stay safe and enjoy your electric bike.
How do electric bikes work

Electric bikes combine the familiar feel of a pedal bike with the power of a motor and a rechargeable battery. When you ride an electric bike, you get help from the motor, which makes pedaling easier and lets you travel farther and faster. The main parts—motor, battery, sensors, and controller—work together to give you a smooth and enjoyable ride. If you want to know how do electric bikes work, you need to understand how each part plays a role in the system.
Main components
Every electric bike has several important parts that work together to help you ride. Here is a table that shows the main components and what each one does:
|
Component |
Function / Contribution |
|---|---|
|
Chain |
Transfers your pedaling power to the rear wheel, moving the bike forward. |
|
Crankset |
Changes your pedaling motion into energy that drives the chain and rear wheel. |
|
Controller |
Acts as the brain, managing how much power goes from the battery to the motor and other parts. |
|
Battery Pack |
Stores electrical energy to power the motor and other systems. |
|
Motor (Rear Hub Motor) |
Turns electrical energy into mechanical energy, giving you extra power and torque. |
|
Brakes (Hydraulic Disc) |
Helps you stop safely and quickly. |
|
Display (LCD) |
Shows speed, battery level, and lets you control pedal assist and other settings. |
|
Pedal Assist Sensors |
Detect when you pedal and tell the motor to help you. |
|
Throttle |
Lets you control the motor power without pedaling. |
|
Frame Parts |
Give the bike structure, strength, and comfort. |
|
Wheels |
Touch the ground and keep you stable. |
|
Suspension |
Absorbs bumps and makes your ride smoother. |
When you ask, "how do electric bikes work," you see that each part has a job. The motor gives you power, the battery stores energy, and the controller decides how much power you get. Sensors and displays help you control the bike and see important information. Good brakes and strong wheels keep you safe and comfortable.
Motor and battery
The electric bike motor is the heart of the system. It takes electrical energy from the battery and turns it into mechanical energy. This process gives you extra power when you pedal or use the throttle. Most e-bikes use hub motors or mid-drive motors. Hub motors sit in the center of the wheel, while mid-drive motors sit near the pedals. Hub motors are the most common, making up about 50-70% of e-bike motors. Mid-drive motors are popular for their smooth power and better hill climbing.
Here is how the motor works:
-
The motor gets electricity from the battery.
-
It spins the wheel or crank, helping you move forward.
-
Sensors and the controller adjust how much power you get, based on how hard you pedal or how fast you go.
The electric bike battery stores the energy needed for your ride. Most e-bike batteries have a voltage between 24V and 52V. Higher voltage batteries give you more speed and power, while lower voltage batteries are lighter and easier to handle. Battery capacity, measured in amp-hours (Ah) or watt-hours (Wh), tells you how far you can go on a single charge. For example, a 48V battery gives you better acceleration and hill climbing than a 36V battery. If you want to ride longer distances, look for a battery with higher capacity, like 15-20Ah.
You need to match the battery to the motor and controller. If you use a battery with too much voltage, you can damage the motor. If the battery is too small, you will not get enough range. E-bike batteries must balance power, range, and weight to fit your needs.
Tip: Always check your battery level before you ride. A fully charged battery gives you the best performance and range.
Sensors and controller
Sensors and the controller make sure your electric bike responds to your actions. They help answer the question, "how do electric bikes work," by making the ride feel natural and safe.
There are different types of sensors on e-bikes:
|
Sensor Type |
Working Principle |
Advantages |
|---|---|---|
|
Torque Sensors |
Measure how hard you pedal using strain gauges. |
Give smooth, natural power that matches your effort. |
|
Central Axis Torque Sensors |
Measure force on both crank arms for high accuracy. |
Very precise and balanced assistance, great for high-performance bikes. |
|
Speed Sensors |
Detect how fast the wheel spins using magnets. |
Simple and effective for matching motor help to your speed. |
|
Contact Speed Sensors |
Use physical contact to sense speed, often with Hall effect sensors. |
Reliable and commonly used in electric bikes. |
Torque sensors give you more power when you pedal harder. Speed sensors increase motor help as you pedal faster. Some e-bikes use both types for the best ride.
The controller acts as the brain of the electric bike. It reads signals from the sensors and decides how much power to send to the motor. When you pedal, the controller checks your effort and speed, then adjusts the motor output. If you use the throttle, the controller gives you power even if you do not pedal. The controller also protects the battery and motor by making sure they do not overheat or get damaged.
You can see your speed, battery level, and assist mode on the display. This helps you control your ride and make smart choices about power and range.
When you put all these parts together, you get a system that makes riding easy and fun. Now you know how do electric bikes work and why each part matters.
Electric bikes operation
Pedal assist system
When you ride an electric bike, the pedal assist system gives you extra power as you pedal. This system uses sensors to detect your pedaling speed, force, and the bike’s speed. The control unit reads this data and tells the motor how much help to give you. You can choose how much assistance you want, making your ride easier or more challenging. Here’s how the pedal assist system works:
-
Sensors (cadence, torque, and speed) detect your pedaling.
-
The control unit processes this information.
-
The motor provides power based on your chosen assist level.
-
You get a smoother ride, easier hill climbs, and longer trips.
Pedal assist levels usually range from 0 to 5. Level 0 means no help from the motor. Levels 1 and 2 give gentle support for flat roads and long rides. Levels 3 and 4 help you climb hills or carry heavy loads. Level 5 gives the most power but uses the battery faster. You can change these levels using the handlebar display.
Throttle mode
Throttle mode lets you ride your electric bike without pedaling. You twist or press a throttle, and the motor gives instant power. This mode feels like riding a scooter. Throttle mode uses more battery because the motor runs whenever you use the throttle, even if you are not pedaling. Pedal assist uses energy only when you pedal, so it saves battery and gives you a more natural ride. The table below shows how much battery each mode uses in different conditions:
|
Riding Condition |
Throttle Mode (Wh/mile) |
Pedal Assist Mode (Wh/mile) |
|---|---|---|
|
Flat Road |
20 |
14 |
|
Moderate Hills |
25 |
18 |
|
Steep Slopes |
30 |
22 |
|
Urban Stop-and-Go |
28 |
20 |
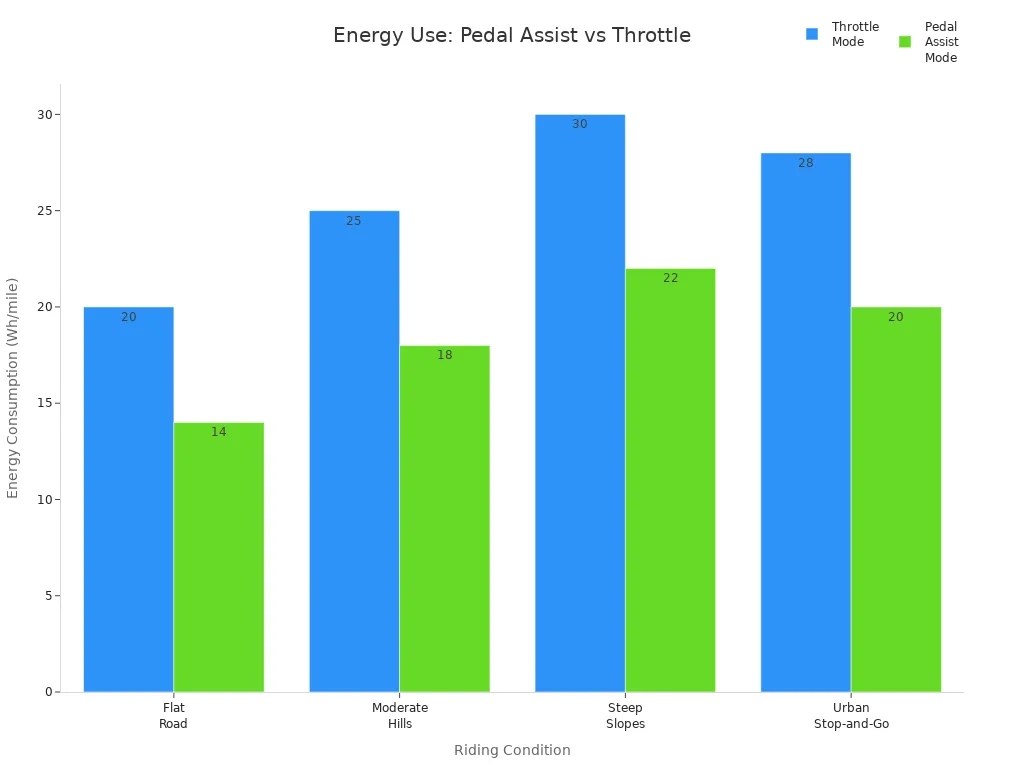
You can see that throttle mode drains the battery faster than pedal assist. For longer rides, pedal assist is the better choice.
Support levels
Support levels let you control how much motorized assistance you get from your electric bike. Higher levels give you more power but use the battery faster. Lower levels help you save battery and ride farther. Here are some tips for using support levels:
-
Use low levels on flat roads to save battery.
-
Switch to higher levels for hills or heavy loads.
-
Keep a steady pace to avoid wasting battery.
-
Shift gears to help the motor work better.
Changing support levels helps you balance comfort, speed, and battery life. You can adjust them anytime during your ride.
Regenerative braking
Some e-bikes have regenerative braking. This feature lets your electric bike recover energy when you slow down. The motor acts as a generator and sends power back to the battery. Regenerative braking can recover about 5-10% of the energy lost during braking. It also helps your brake pads last longer and gives smoother stops. The table below compares regular braking and regenerative braking:
|
Feature |
Traditional E-Bike Braking |
E-Bikes with Regenerative Braking |
|---|---|---|
|
Energy Recovery |
None |
5-10% of braking energy |
|
Battery Range Extension |
None |
5-10% increase in ideal cases |
|
Brake Pad Wear |
Higher |
Lower |
|
Best Use |
N/A |
High speeds, downhill |
Regenerative braking does not replace normal brakes, but it helps you get a little more range from your battery.
Using an e-bike
Turning on and off
You start your electric bike by pressing the power button, usually found on the display or near the battery. Some models require you to unlock the battery first. Once powered on, the display lights up and shows your battery level. To engage the motor, you can begin pedaling or use the throttle if your electric bike has one. When you finish your ride, set the pedal assist to zero or turn off the power completely. Always power down your electric bike before parking to prevent accidental motor activation.
Electric bikes include many safety features to protect you and your battery. Here is a table showing some common features and their benefits:
|
Safety Feature |
Description and Safety Benefit |
|---|---|
|
Adjustable Handlebars and Stem |
Lets you find a comfortable position for better control. |
|
Quick-Release Seat Post |
Makes it easy to adjust saddle height for a good fit. |
|
Battery Management Systems |
Protects your battery from overcharging, overheating, and short circuits. |
|
Removable Batteries |
Lets you charge your battery indoors and keeps it safe from theft. |
|
Speed Limiters and Motor Cut-Off |
Limits speed and cuts motor power when you brake for safety. |
|
Hydraulic Disc Brakes |
Gives strong and reliable stopping power. |
|
Integrated Lighting |
Improves your visibility with front and rear lights. |
|
Pedal Assist Technology |
Delivers smooth power to avoid sudden bursts. |
|
Wide Tires |
Increases stability and absorbs bumps. |
Tip: Always check your battery level before you ride. A full battery helps you avoid running out of power during your trip.
Selecting assistance
You can choose different assistance levels on your electric bike using the handlebar display. These levels control how much help the motor gives you. Lower levels use less battery and let you do more of the work. Higher levels give you more power, which helps on hills or when you feel tired, but they use more battery.
When you pick an assistance level, think about your riding style and the terrain. Some riders like a low cadence with high torque for climbing hills. Others prefer a high cadence for steady cruising. Your electric bike may have pedal assist or throttle options. Pedal assist lets you adjust effort and save battery for longer rides. Throttle gives quick bursts of power but drains the battery faster. Always consider your battery range, the type of electric bike, and local speed limits when choosing your assistance level.
Riding basics
Riding an electric bike safely and efficiently takes practice. Start by managing your speed. Ride slower in crowded areas and use higher speeds only on open roads. Approach turns carefully and slow down before curves. Plan your braking early, especially near intersections. Stay alert for hazards like potholes, debris, or cars. Use hand signals to show your intentions and make sure you stay visible, especially in low light.
Wear a helmet and protective gear for safety. Check your tires, battery, and brakes before every ride. Adjust your saddle and handlebars for comfort. Make sure your battery is charged and your electric bike is in good condition. Follow all traffic laws and use lights and reflectors to stay visible. These habits help you get the most from your electric bike and keep you safe on every ride.
Electric bike benefits and limits
Riding without power
You can ride your electric bike even when the battery runs out. On flat roads, pedaling feels almost the same as a regular bike, but you will notice the extra weight. The heavier frame and motor add more resistance, especially when you go uphill. Some motors, like geared hub motors, have little drag, so you can pedal smoothly. Direct drive motors create more resistance, making it harder to ride without power. If you ride without assistance, you will burn almost as many calories as on a regular bike, but the extra weight means you work a bit harder, especially on hills.
Tip: If you want to optimise the range of my electric bike, use lower assist levels and pedal more on flat terrain.
Charging and battery life
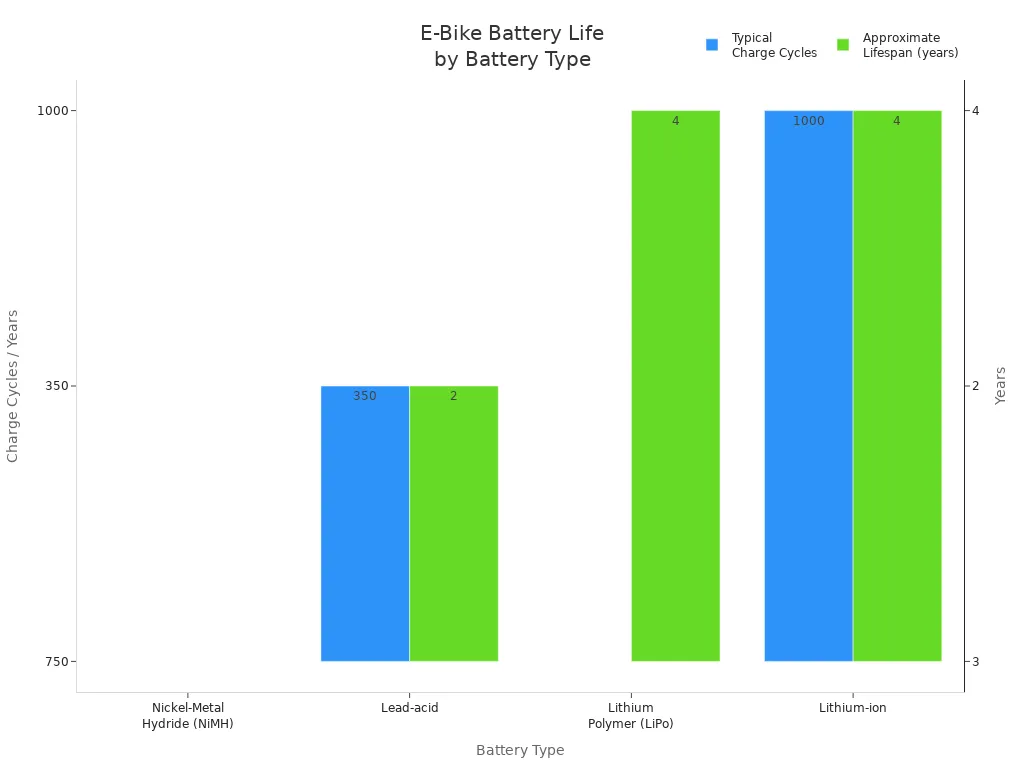
Charging your electric bike battery is simple, but you need to follow some steps to keep it healthy. Most batteries last between 500 and 1,500 charge cycles, depending on the type and model. For example, lithium-ion batteries can last up to five years if you take care of them. Charging time depends on the battery size, charger type, and temperature. Fast chargers can reduce charging time, but always use a charger that matches your battery. Try to keep your battery between 20% and 80% charged. Avoid letting it fully discharge or stay at 100% for long periods. Store your battery in a cool, dry place when not in use.
|
Battery Type |
Typical Charge Cycles |
Approximate Lifespan |
|---|---|---|
|
Nickel-Metal Hydride |
500 - 1,000 |
2 - 4 years |
|
Lead-acid |
200 - 500 |
1 - 3 years |
|
Lithium Polymer |
500 - 1,000 |
3 - 5 years |
|
Lithium-ion |
500 - 1,500 |
3 - 5 years |
Speed and legal rules
Electric bike speed limits and laws change depending on where you live. In the United States, most electric bikes fall into three classes. Class 1 and Class 2 electric bikes help you up to 20 mph. Class 3 electric bikes can reach 28 mph with pedal assist. In Europe, standard electric bikes can go up to 25 km/h (about 15.5 mph) with a 250-watt motor. Faster models, called speed pedelecs, need insurance and registration. Always check local rules about helmets, age limits, and where you can ride. Following these rules keeps you safe and avoids fines.
|
Country |
Speed Limit (km/h) |
Speed Limit (mph) |
Helmet Requirement |
Registration/Insurance |
Age Restriction |
Road Use Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
USA |
32 (Class 1/2), 45 (Class 3) |
20, 28 |
Varies by state |
No (except speed pedelecs) |
Varies by state |
Bike lanes/roads (check local laws) |
|
Germany |
25 (standard), 45 (speed pedelec) |
15.5, 28 |
Mandatory for speed pedelecs |
Required for speed pedelecs |
Minimum 15 years |
Standard e-bikes on bike lanes; speed pedelecs on roads only |
Maintenance
Taking care of your electric bike helps it last longer and keeps you safe. You should check the tires, brakes, and chain often, just like with a regular bike. The battery needs special care. Charge it regularly, avoid deep discharges, and store it at 30-60% charge if you will not use it for a while. Keep the battery and motor clean and dry. Do not use high-pressure water near the electrical parts. The heavier weight and extra power mean you need to check the brakes and chain more often. Schedule regular tune-ups, and ask a professional for help with electrical repairs.
-
Check tire pressure and brake pads every week.
-
Clean the chain and gears after wet rides.
-
Wipe the battery and motor with a dry cloth.
-
Never flip your electric bike upside down to wash it.
-
Store your electric bike indoors to protect the battery from extreme temperatures.
Note: Good maintenance reduces repair costs and helps your electric bike run smoothly for years.
Pedal bike with motor vs regular bike
Handling and feel
When you ride a pedal bike with motor, you notice some differences compared to a regular bike. The extra weight from the motor and battery changes how the bike feels, especially at slow speeds. You may feel the bike is heavier, but most e-bikes balance this weight well. The riding position and frame design affect your comfort and stability. Test the bike at different speeds to see if it feels top-heavy or steady.
-
The type of sensor matters. Torque sensors give you smooth, natural pedal assist. Cadence sensors can feel more abrupt when the motor kicks in.
-
Good motors provide steady power, especially when starting from a stop or climbing hills.
-
Hydraulic disc brakes help you stop quickly and safely.
-
Quiet motors and solid frames make your ride more enjoyable.
E-bikes look and ride much like regular bikes, but you get more power and a bit more weight. When the battery runs out, you can still pedal, but you will feel the extra resistance. Riders who like resistance training may not mind the added weight.
Range and effort
Electric bikes let you travel farther with less effort than regular bikes. The motor gives you a boost, so you do not get tired as quickly. You can ride up hills and cover longer distances without feeling worn out. The range depends on the battery size, your weight, the terrain, and how much assistance you use.
|
eBike Model/Power |
Typical Range on Single Charge |
Factors Affecting Range |
Effort Compared to Regular Bike |
|---|---|---|---|
|
General eBikes |
22-50 miles |
Battery, terrain, rider weight, riding style |
Less effort, longer rides |
|
1000W eBike |
30-40 miles (up to 70 ideal) |
Rider weight, terrain, pedaling, speed, battery size |
Much less effort, faster travel |
|
750W eBike |
19-25 miles (up to 40) |
Terrain, battery, speed |
Easier pedaling, good for all fitness levels |
You can adjust the assist level to save battery or get more help. Lower assist levels let you ride farther, while higher levels use more battery but make pedaling easier. Steep hills, rough roads, and heavy loads reduce your range. Regular bikes rely only on your muscle power, so you may get tired faster and travel shorter distances.
Tip: Use lower assist levels on flat roads to extend your range and get some exercise.
Electric bikes use a motor, battery, sensors, and controller to give you extra power while you ride. You can climb hills, travel farther, and enjoy cycling with less effort.
-
E-bikes help you stay active, ride with friends, and reduce your carbon footprint.
-
You should brake earlier, use lower assist modes, and check your bike often for safety.
-
Wear a helmet, follow local rules, and signal before turning.
Many people find e-bikes fun and easy to use. Try one for yourself and discover a new way to enjoy cycling!
FAQ
How far can you ride on a single charge?
Most electric bikes let you ride between 20 and 50 miles per charge. Your range depends on battery size, assist level, your weight, and the terrain. Using lower assist levels helps you go farther.
Can you ride an electric bike in the rain?
Yes, you can ride most electric bikes in the rain. The electrical parts have water-resistant covers. You should avoid deep puddles and dry your bike after wet rides to keep it in good shape.
Do you need a license to ride an electric bike?
In most places, you do not need a license for standard electric bikes. Some faster models may require registration or insurance. Always check your local laws before you ride.
How long does it take to charge an electric bike battery?
Charging usually takes 3 to 6 hours. The time depends on your battery size and charger type. Fast chargers work quicker, but always use the charger that comes with your bike for safety.
What maintenance does an electric bike need?
You should check your tires, brakes, and chain often. Keep the battery clean and charged. Wipe the motor with a dry cloth. Schedule regular tune-ups to keep your electric bike running smoothly.






 S2
S2
 KS4 Pro
KS4 Pro
 MAX Pro
MAX Pro



 Light-Weight & Portable
Light-Weight & Portable
 Long Range
Long Range
 For Heavy Riders
For Heavy Riders
 Big Wheel
Big Wheel
 With Seat
With Seat
 Fast
Fast



 EX6
EX6
 P6
P6
 C1
C1
 S2 Lite
S2 Lite
 BK1
BK1
 ES-1
ES-1
 DK1
DK1










Leave a comment
All comments are moderated before being published.
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.